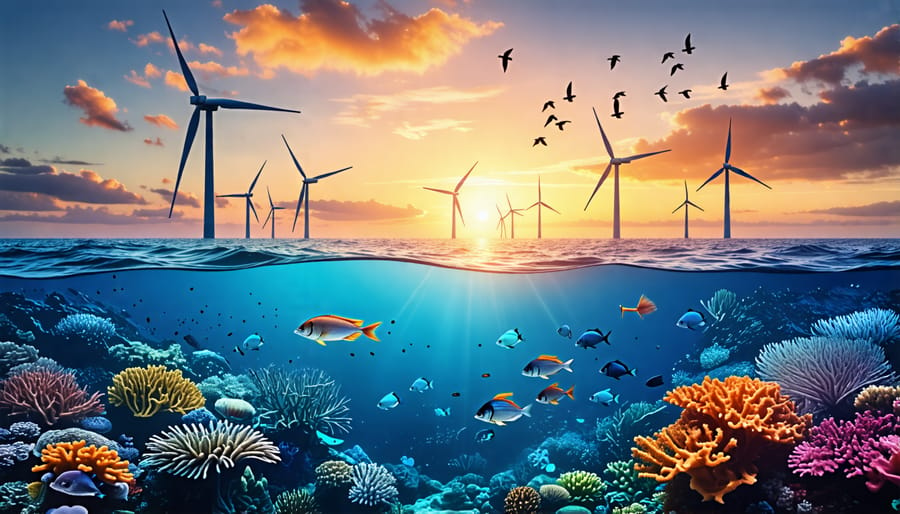
Offshore wind farms offer a promising sustainable energy solution, but their environmental impact is a complex issue that deserves careful examination. While these coastal turbines harness the immense power of ocean winds to generate clean electricity, they also interact with delicate marine ecosystems in ways that are not yet fully understood.
As the world increasingly turns to renewable energy to combat climate change, it is crucial that we develop offshore wind responsibly, with a clear-eyed understanding of both the benefits and potential ecological risks. Only by weighing these considerations can we chart a course towards a future powered by the wind, in harmony with the rhythms of the sea.
How Offshore Wind Farms Work

Turbine Design and Components
Offshore wind turbines are engineered to withstand harsh marine conditions while maximizing energy generation. The key components include the foundation, which anchors the structure to the seabed using monopiles, gravity-based systems, or floating platforms. The tower, typically made of steel or concrete, supports the nacelle housing the gearbox, generator, and other mechanical components. The turbine design incorporates three blades, often exceeding 80 meters in length, made from lightweight composite materials like fiberglass or carbon fiber. These blades are optimized to capture wind energy efficiently, with advanced airfoil shapes and pitch control systems. The nacelle also contains a yaw drive to orient the rotor towards the wind, while the power electronics and transformer convert the generated electricity for transmission to shore via undersea cables. Continuous monitoring systems and regular maintenance ensure optimal performance and longevity in the challenging offshore environment. As technology advances, innovations in materials, control systems, and foundation designs are enabling the development of larger, more efficient turbines that can harness the vast wind resources found in deeper waters farther from the coast.
Energy Generation and Distribution
Offshore wind turbines harness the kinetic energy of wind to generate electricity. As the wind blows, it turns the turbine blades, which spin a shaft connected to a generator. The generator converts this mechanical energy into electrical energy. Undersea cables then transmit the electricity to shore, where it is distributed to homes and businesses through the power grid. Offshore substations may be used to collect and stabilize the power before it reaches land. By capturing the abundant, consistent winds found at sea, these turbines provide a reliable, renewable source of energy with minimal land use impact.
Environmental Benefits
Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Offshore wind energy plays a vital role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions by replacing fossil fuel-based electricity generation. As wind turbines harness the vast, renewable power of ocean winds, they generate clean electricity without releasing carbon dioxide or other harmful pollutants. By displacing coal, oil, and natural gas, offshore wind farms significantly lower the carbon footprint associated with meeting our energy needs.
A single offshore wind turbine can prevent thousands of tons of carbon dioxide emissions annually, equivalent to taking hundreds of cars off the road. As more offshore wind projects come online, they contribute to a growing share of low-carbon electricity in the grid mix. This helps nations meet their climate targets and transition to a sustainable energy future.
Moreover, the scalability of offshore wind allows for substantial emissions reductions. With larger turbines and higher capacity factors than onshore installations, offshore wind farms can generate immense amounts of clean power. As technology advances and costs decline, the potential for offshore wind to displace fossil fuels and mitigate climate change grows even greater.
By embracing offshore wind as a key solution in the fight against global warming, we can make significant strides in reducing our greenhouse gas emissions and creating a cleaner, more sustainable world for future generations.
Improved Air and Water Quality
Offshore wind farms play a significant role in improving local air and water quality by reducing reliance on fossil fuels. Unlike coal or natural gas power plants, wind turbines generate electricity without emitting harmful pollutants such as carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide, and nitrogen oxides. By displacing these conventional energy sources, offshore wind farms contribute to cleaner air in coastal communities, reducing the risk of respiratory illnesses and acid rain.
Moreover, offshore wind farms help combat water pollution by minimizing the need for coal mining and natural gas extraction, which can contaminate water sources through acid mine drainage and fracking. The decreased demand for these activities helps preserve the integrity of local watersheds and marine ecosystems.
Furthermore, the ocean-based location of offshore wind farms allows for cooler, steadier winds, leading to more efficient power generation compared to onshore installations. This increased efficiency translates to a greater displacement of fossil fuels and their associated pollutants per unit of energy produced.
As governments and organizations continue to prioritize the development of offshore wind power, the positive impact on regional air and water quality will only grow. By embracing this clean energy solution, communities can enjoy the benefits of improved public health and a more sustainable future.
Potential Ecological Concerns
Impact on Bird and Bat Populations
Offshore wind farms can potentially impact bird and bat populations through collision risks and habitat disruption. Birds, particularly migratory species, may collide with turbine blades during flight, leading to injury or mortality. However, studies suggest that the impact on bird populations is relatively low compared to other human-related causes. Bats, attracted to insects around turbines, are also at risk of collision or barotrauma from rapid air pressure changes near the blades. Careful site selection and monitoring can help mitigate these risks. Additionally, the physical presence of turbines and underwater noise during construction may temporarily disrupt feeding and breeding habits of some species. Long-term research is crucial to understand and address these concerns, ensuring that offshore wind development proceeds in harmony with the delicate marine ecosystem.
Effects on Marine Mammals and Fish
Offshore wind farms can have mixed effects on marine mammals and fish. While some studies suggest that the noise from construction and operation may temporarily disrupt communication and navigation for cetaceans like whales and dolphins, long-term impacts appear minimal. In fact, the underwater structures can create artificial reefs, providing new habitats and feeding grounds for various species. A prime example is the Block Island Wind Farm off Rhode Island, where researchers observed an increase in fish populations and even found seals using the turbine bases as resting spots.
However, proper planning and monitoring are crucial to mitigate any potential negative consequences. Developers should conduct thorough environmental impact assessments and work with marine biologists to choose locations that minimize habitat disturbance. Additionally, implementing “soft-start” procedures during construction can give animals time to leave the area, reducing noise exposure. As we continue to harness the immense potential of offshore wind energy, prioritizing the well-being of marine life will be key to ensuring a sustainable future for our oceans and the incredible biodiversity they support.
Invasive Species and Reef Effects
The introduction of offshore wind turbines can lead to the development of artificial reef ecosystems, attracting various marine species. While this may seem beneficial, there are concerns about the potential for non-native or invasive species to colonize these structures. These species can disrupt the delicate balance of existing reef communities, competing for resources and altering food webs. Studies have shown that wind farm foundations can serve as stepping stones for invasive species, facilitating their spread across previously disconnected areas. To mitigate these risks, ongoing monitoring and proactive management strategies are crucial. This includes regular inspections of turbine structures, early detection and removal of invasive species, and the use of materials that discourage colonization by unwanted organisms. By addressing these concerns and implementing best practices, offshore wind farms can minimize their impact on reef ecosystems and protect the biodiversity of our oceans.
Mitigation Strategies and Responsible Development
Careful Site Selection
Careful site selection is crucial for minimizing the environmental impact of offshore wind farms. Developers must work closely with marine biologists and ecologists to identify locations that avoid sensitive habitats, such as coral reefs, seagrass beds, and fish spawning grounds. Additionally, they should steer clear of migration routes used by whales, dolphins, and seabirds to prevent disruptions to their natural behaviors. By conducting thorough environmental impact assessments and engaging in stakeholder consultations, wind farm planners can select sites that strike a balance between optimal wind resource utilization and ecological preservation. This approach ensures that offshore wind energy can be harnessed sustainably, without compromising the delicate marine ecosystems that are vital to the health of our planet.
Wildlife-Friendly Design Modifications
Wildlife-friendly design modifications can significantly reduce the impact of offshore wind farms on marine life. Adjustments like using larger, slower-turning blades and painting turbine blades to increase visibility have shown promise in minimizing bird and bat collisions. Carefully timing construction and maintenance activities around migration seasons can further protect vulnerable species. Innovative solutions like bubble curtains and hydro sound dampers help mitigate underwater noise pollution during installation. By incorporating these thoughtful design changes and adopting best practices for responsible operation, offshore wind developers can work in harmony with the delicate marine ecosystem while harnessing the immense potential of this clean energy source.
Environmental Monitoring and Adaptive Management
Offshore wind farm developers employ rigorous environmental monitoring programs to track and mitigate any adverse effects on marine ecosystems. These environmental monitoring initiatives involve regular surveys of wildlife populations, underwater noise levels, and sediment transport. By gathering and analyzing this data, project managers can identify potential issues early on and implement adaptive management strategies to minimize ecological disturbances. This proactive, science-based approach ensures that offshore wind energy remains a sustainable solution, balancing the need for clean power with the preservation of precious marine habitats.

Conclusion
Offshore wind power is a crucial renewable energy solution in the fight against climate change. As we continue to expand this technology, it is essential to prioritize responsible development that minimizes negative environmental impacts and protects delicate marine ecosystems. By conducting thorough environmental assessments, utilizing eco-friendly materials and construction methods, and carefully selecting wind farm locations, we can harness the immense potential of offshore wind while safeguarding the health and biodiversity of our oceans. As we move forward, ongoing research, monitoring, and collaboration between industry, government, and environmental organizations will be key to ensuring the sustainable growth of offshore wind power for a cleaner, greener future.





